We have all seen brands changing their questionable names into ‘Smart’ and ‘Glow’, even though the composition is still bad for our skin. But even after changing the names, the people who are still willing to purchase such face creams remain the same. The only unchanging factor is the obsession with fairness, skin lightening, and instant brightness. Of course, we acknowledge that some people struggle with acne marks and melasma, and for that, our audience has evolved as they are now purchasing another fancy set of products with chemical ingredients.
Now the target is skipping cosmetic creams and focusing on products that are ‘Medicated Creams.’
Yes, medicated creams have taken over the obsession with clear and fair skin, as the ingredients in them are more effective and fast-acting. These ingredients work faster and give instant results.
But if you’re a person with no prescription, no melasma, no dark spots due to burns or excessive scarring, then why are you using those creams?
People with no knowledge of what those over-the-counter creams can do to their skin in the long run are as naive as those who are using cosmetic fairness products.
Let us understand what components are there in those Over the counter creams and how do they affect our skin.
These over-the-counter medicated creams contain high-end chemicals that scrape off the top layer of the skin and expose the skin underneath to the environment.
“Now, when we talk about healthy skincare, we should be emphasizing how to protect the skin and restore the skin barrier, but here, we are doing the opposite.”
What are the OTC cream ingredients you should not apply without a dermatologist’s prescription?
Hydroquinone
- Use: Skin lightening agent for hyperpigmentation.
- Risks: Skin irritation, redness, burning, and potential depigmentation. Prolonged use may lead to ochronosis, a condition causing bluish-black discoloration of the skin.
Topical Steroids (Betamethasone, Clobetasol, Mometasone)
- Use: Reduce inflammation and treat various skin conditions.
- Risks: Skin thinning, increased susceptibility to bruising, and potential hormonal imbalances. Overuse can lead to steroid-induced rosacea and acne.
Parabens
- Use: Preservatives to prevent microbial growth.
- Risks: Endocrine disruption, reproductive toxicity, and potential links to breast cancer.
Phthalates
- Use: Enhance flexibility and softness in products.
- Risks: Hormonal disruptions, liver and kidney damage, and developmental issues.
Formaldehyde Releasers (DMDM Hydantoin, Imidazolidinyl Urea)
- Use: Preservatives that release formaldehyde to prevent microbial growth.
- Risks: Skin irritation, allergic reactions, and potential carcinogenic effects.
Oxybenzone & Octinoxate
- Use: UV filters in sunscreens and SPF products.
- Risks: Hormonal disruptions and potential environmental harm, particularly to coral reefs.
Benzoyl Peroxide
- Use: Treat acne by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation.
- Risks: Recent studies have found that some benzoyl peroxide products contain high levels of benzene, a known carcinogen.
OTC Face Creams To Avoid Without Prescription

- Melalite Forte: Contains 4% hydroquinone.
- Depiwhite Cream: Includes 2% hydroquinone, kojic acid, and other agents.
- Melapik-HQ: Formulated with 4% hydroquinone.
- Hyde Cream: Contains hydroquinone.
- Skinlite Cream: A combination of hydroquinone, tretinoin, and mometasone.
- Eukroma: Features 4% hydroquinone.
- Moon Glow: Hydroquinone 2%
- No Scars: Hydroquinone 2%, tretinoin, and mometasone Furoate.
There are many more OTC creams which are available choose to apply only if the dermatologist suggests.
What Happens to Your Skin in the Long Term
In the first week of application, you might notice that your dark spots are lightened and there is a glow on your face. You may also see your skin tone become slightly fairer.
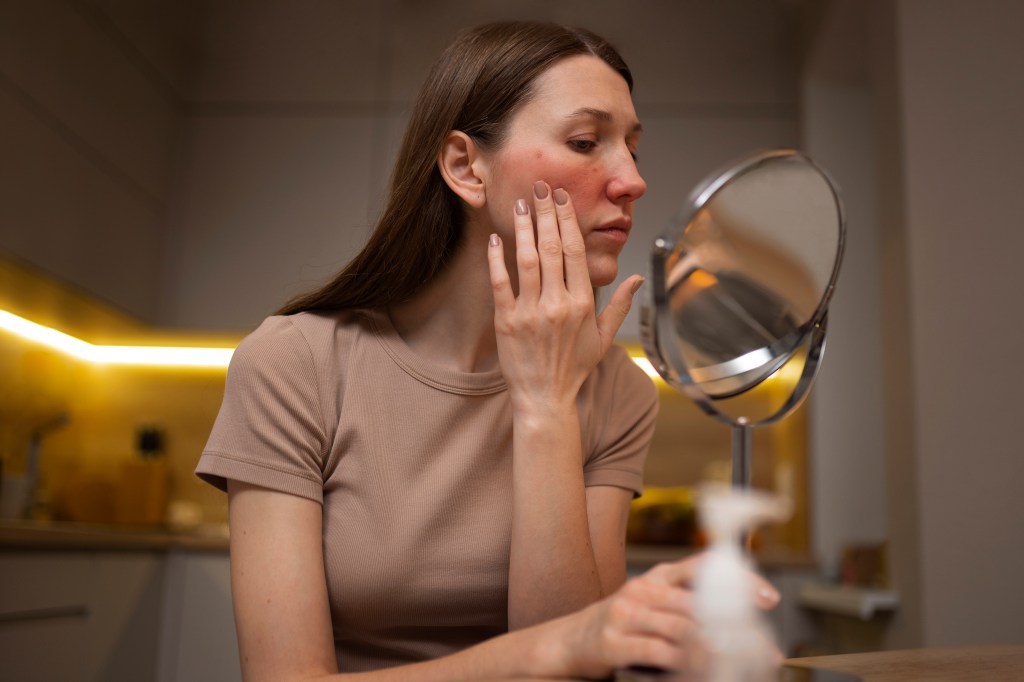
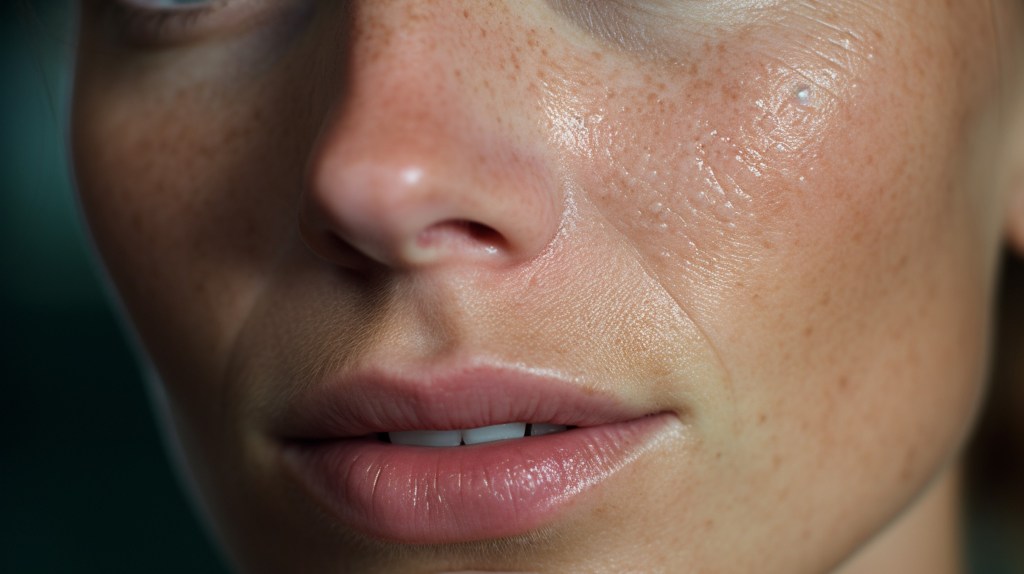
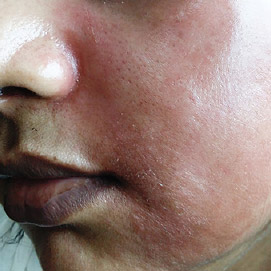
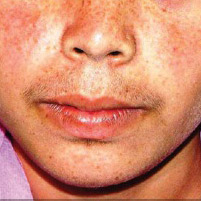
However, after 2-3 weeks of use, your skin will have lost its “skin barrier,” and it will start to thin. You may experience redness on your face when exposed to the sun.
At this point, all the dirt and pollution will settle on the irritated skin that you exfoliated with the OTC cream.
Now, understand how your skin becomes darker after using such creams.
When you discontinue the cream (and I would suggest doing so as soon as possible), your skin will be fully exfoliated and new. Your skin will signal to your brain that it is injured and needs to repair itself. This is when the component melanin is released, which helps build the skin. Melanin is responsible for creating pigmentation, which helps in repairing the skin.
It is highly likely that the pigmentation will take months to heal, so be very careful about what you use on your face.






Leave a Comment